What should you look for when choosing sunscreen?
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesTemperatures are set to rise this week in many parts of the UK, and UV levels are expected to be high.
How can you protect your skin from the sun's rays?
What do the SPF numbers mean on sunscreen?
The most prominent number on sunscreen bottles is the sun protection factor or SPF.
The higher the number, the greater the protection it offers.
SPF tells you how much protection your sunscreen provides from UVB radiation. The number refers to how much UVB it allows in, not how much it blocks.
For example, a sunscreen with SPF 15 allows one-fifteenth of the sun's rays to reach your skin, or about 7%.
So it filters out about 93% percent of UVB rays while SPF 30 filters about 97%.
This means if you could stay in the sun for 10 minutes unprotected without burning, SPF 15 would in theory give you 15 times that protection, or two-and-a-half hours before you would burn.
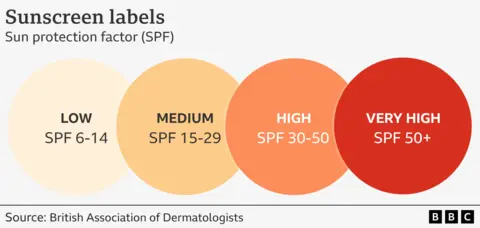
The British Association of Dermatologists says sunscreen with SPF 30 is a "satisfactory form of sun protection in addition to protective shade and clothing".
It says sunscreen should be reapplied at least every two hours, regardless of its SPF.
What are UVA and UVB and what do the star ratings mean?
Many brands also carry a star rating from one to five.
This tells you the percentage of UVA radiation that is absorbed by the sunscreen in comparison to how much UVB is absorbed. The more stars the better.
UVA and UVB refer to different wavelengths of radiation from the sun that enter the Earth's atmosphere.
UVA is associated with ageing of the skin and pigmentation as well as skin cancer. It can affect human skin even through glass.
UVB causes sunburn, and is linked to particular types of skin cancer - basal cell carcinoma (the most common type) and malignant melanoma.
A low SPF sunscreen could have a high star rating if the ratio of UVA to UVB protection is the same as in a higher SPF product.
Ideally, you want a sunscreen with a high SPF and a high star rating.
How effective is the best sunscreen?
These levels of protection assume sunscreen has been applied in ideal conditions.
In reality, most people do not apply sunscreen perfectly, and it can rub off with sweat or while in water.
Experts think most people only apply half the recommended quantity.
You should not use sunscreen which is past its expiry date as it may be less effective.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesEU guidance states that sunscreen should only be marketed as having sun protection of "50+" and not the ratings of 80 or 100 which can be found in some countries.
It thinks these could be misleading about how much extra protection they provide: SPF 50 provides about 98% protection, while SPF 100 would provide less than 100%.
No product provides 100% protection from the sun's rays so the advice is that everyone should cover up and seek shade when the sun is strongest.
What about 'once-a-day' sunscreens?
There are lots of "extended wear" sunscreens on the market that advertise themselves as being for use "once a day". Many claim to offer protection for up to eight hours - if applied correctly.
But some dermatologists recommend that these products should still be applied at least every two hours, like any other sunscreen, since the risk that you may have missed a spot - or that it will rub or wash off in that time - are too high.
A Which? report in 2016 criticised four of these products for not providing the protection promised. It found that after six to eight hours, the average protection offered decreased by 74%.
But this claim was rejected by some of the manufacturers, who said their own testing had produced different results.
